1. Clinical Decision Making (CDM), Planning and Managing cases of Infected Non union of Radius & Ulna?
2. Technical Tips and Pearls of Surgical management in such cases and how to prevent such cases?
Dr.Mangal Parihar, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Swastik Park, Chembur, Mumbai -400071.Email: mangalparihar@gmail.com
Introduction: Infected nonunion of radius and ulna are rare but difficult problems to deal. We report a case of successfully managed infected non-unonion of forearm bones and the reasoning behind strategy of approach to the case.
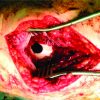
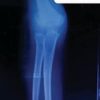
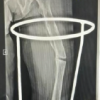
Case Report: 42 year old female presented with history of closed forearm fracture three months back for which she was operated with open reduction and internal fixation using dynamic compression plate. There was pain and fever post-surgery and discharge and wound gape. This was treated with resuturing of the wound and oral antibiotics. She continued to have pain fever and discharge and consulted another surgeon who removed first the radius plate and then the ulna plate sequentially with stabilisation by external fixation. She presented to us at three months post injury with infected nonunion of radius and ulna with loosening of fixators, sequestrum on radiograph and wristdrop. A staged treatment was planned for her. As first stage debridement, antibiotic Calcium Sulphate cement bead insertion and intramedullary flexible nail fixation. She was given iv antibiotics as per culture report. At 3 months post surgery the infection had settled and pellets were resorbed. Double barrel vascularized fibula graft was used to fill the gap and fixation using long locked plates was done. At one year follow up radiographs showed good healing and clinically patient was able to carry out all her activities.
Conclusion: Proper planning and staged management of such cases helps to achieve goals with good functional outcome.
Keywords: Infected nonunion, radius, ulna, vascular fibula graft.