[box type=”bio”] What to Learn from this Article?[/box]
1. A new technique for reduction of displaced dorsal fragment in distal radius fracture through volar bone fenestration?
2.Result of two such cases done by the same technique?
Case Report: Volume 3 | Issue 2 | JOCR April – June 2013 | Page 8-11 | Tsuchiya F, Naito K, Mogami A, Obayashi O
Authors: Fumika TSUCHIYA[1,2], Kiyohito NAITO[1], Atsuhiko MOGAMI[1], Osamu OBAYASHI[1]
[1]Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Juntendo University Shizuoka Hospital, 1129 Nagaoka, Izunokuni, Shizuoka, 410-2295 Japan.
[2]Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Niigata City General Hospital, 463-7 Shumoku, Chuo-ku, Niigata 950-1197 Japan.
Address of Correspondence:
Dr Kiyohito NAITO: Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Juntendo University Shizuoka Hospital, 1129 Nagaoka, Izunokuni, Shizuoka, 410-2295 Japan. E-mail : knaito@juntendo.ac.jp
Abstract
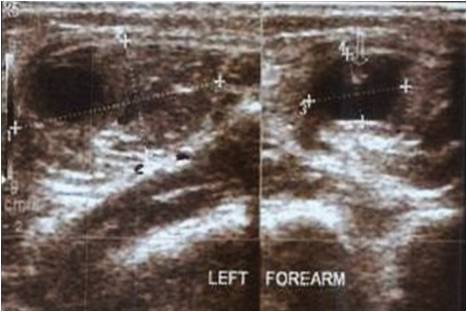
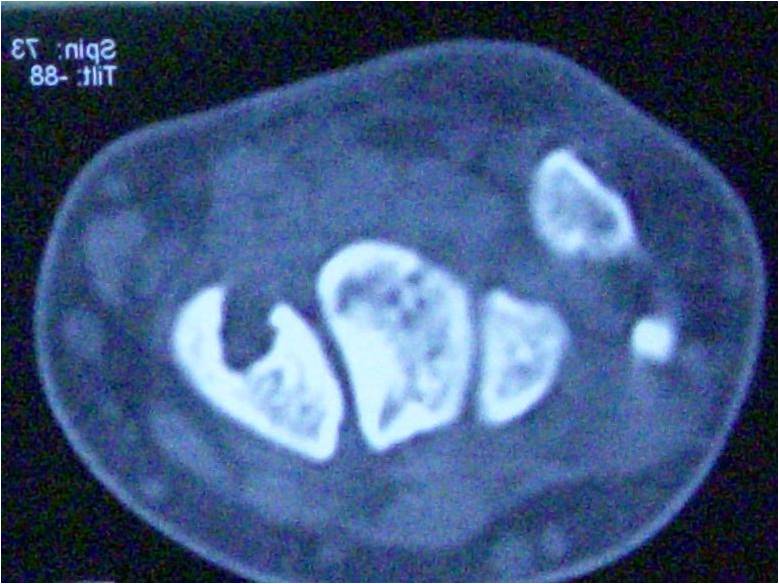
Introduction: For intra-articular distal radius fractures (AO Classification, type B2) with a displaced dorsal fragment, there remains much discussion on the fixation method for the dorsal fragment. To reduce the displaced dorsal fragment, we developed a new technique consisting of fenestration of the volar bone cortex, reduction using an intramedullary procedure, and fixation using a volar plate.
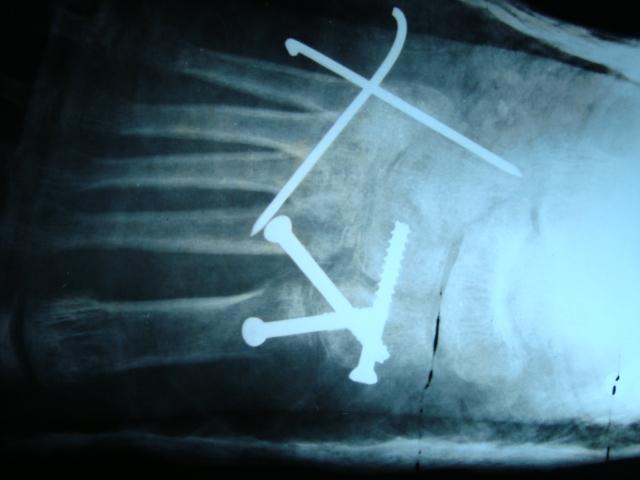
Case Report: We performed this surgical technique in 2 patients and achieved a good reduced position without much injury to the bone cortex at the site of volar plate placement. This surgical technique allows reduction of the dorsal fragment using an intramedullary procedure by only a volar approach, and, therefore, does not affect the dorsal soft tissue (extensor tendon). For intra-articular distal radius fractures, complete reduction of the articular surface is extremely difficult, and, in patients with a remaining gap on the articular surface, a variable angle locking screw system may be useful. In the 2 patients, the angle of the locking screw was adjusted to catch the displaced dorsal fragment, and adequate reduction and fixation could be achieved.
Conclusion: This technique, in which fenestration of the volar bone cortex allows a reduction procedure for the dorsal fragment, was useful for the reduction and fixation of the displaced dorsal fragment in distal radius fractures.
Keywords: volar plate, distal radius fracture, dorsal fragment, intramedullary reduction procedure.
|
How to Cite This Article: Tsuchiya F, Naito K, Mogami A, Obayashi O. New Technique for Dorsal Fragment Reduction in Distal Radius Fractures by Using Volar Bone Fenestration. J Orthopaedic Case Reports 2013 April-June;3(2):8-11. Available from : https://www.jocr.co.in/wp/2013/04/13/2250-0685-093-fulltext/ |
(Figure 1) | (Figure 2) | (Figure 3) | (Figure 4)
[Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]
[rate_this_page]
Dear Reader, We are very excited about New Features in JOCR. Please do let us know what you think by Clicking on the Sliding “Feedback Form” button on the <<< left of the page or sending a mail to us at editor.jocr@gmail.com