[box type=”bio”] What to Learn from this Article?[/box]
Presentation and Diagnosis of Shoulder Tuberculosis.
Case Report | Volume 3 | Issue 4 | JOCR Oct-Dec 2013 | Page 23-25 | Deshmukh A, Deo S, Salgia AK, Agarwal T
DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.126
Authors: Deshmukh A[1], Deo S[1], Salgia AK[1], Agarwal T[1]
[1]Department Of Orthopaedics, Dr.D.Y.Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune. India.
Address of Correspondence:
Dr Ashwin Deshmukh, Assistant Professor, E-604, Mahindra Royale Society, Opp Hindustan Antibiotic ground, Off Ajmera, Pimpri, Pune 411018. India. Email: drashwin_d@yahoo.com
Abstract
Introduction: Afflictions of shoulder by tuberculosis is rare and when it occurs its more commonly a dry lesion (caries sicca). Wet lesions in shoulder are rare and we report this case for the rarity of its occurrence.
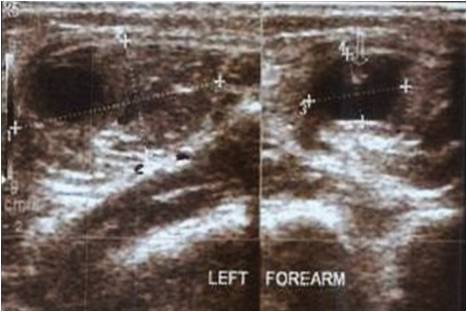
Case Report: A 55yrs old female patient presented with a painful swelling with restriction of movements of the right shoulder since six months. Patient had taken various treatments without any relief; there was no history of trauma, weight loss, recent infection in the past or any history of tuberculosis in family or contact with tubercular patient. Right shoulder revealed restricted movements with no local rise in temperature. Tenderness was present over anterior and posterior aspect of the right shoulder diffusely. External rotation and abduction movements were restricted while adduction and flexion were not restricted. Power of the muscles was unaffected with no neurological deficit. Antero-posterior and axial X-rays of the right shoulder showed no bony involvement however, ultrasonography showed lipoma. Serological investigations showed a markedly raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate (73mm / hr) and a positive C-reactive protein. Surgical excision of the mass revealed rice bodies. DNA PCR was positive for tuberculosis and patient was started on anti-tubercular treatment( Category I) for six months.
Conclusion: Any patient coming with the complaints of long standing painful restriction of the movements of the shoulder associated with or without complaints swelling, shall be evaluated to rule out skeletal tuberculosis along with other differential diagnosis of periarthritis of shoulder and adhesive capsulitis. Most of the patients with skeletal tuberculosis may not necessarily present with the constitutional symptoms of fever, weight loss, etc and also because of the widespread prevalence of the organism in India.
Keywords: Shoulder Tuberculosis, Caries Sicca, rice bodies.
Introduction
Out of all the skeletal tuberculosis, 50% accounts for the spinal tuberculosis and rest 50% accounts for the tuberculosis of the joints (sacroiliac joint, hip joint, knee joint, shoulder joint, elbow joint, wrist joint) tuberculosis of the small bones(metatarsus, metacarpus and the phalanges), tuberculosis of the tendon sheaths and bursae and the tuberculous osteomyelitis. Tuberculosis of the shoulder is a very rare manifestation of the extra pulmonary tuberculosis. It varies from an incidence rate of 0.9 to 1.7% [1,2].out of the total extra pulmonary tuberculosis. The variants of extra pulmonary or skeletal tuberculosis are the classical dry type/atrophic type (Caries Sicca) 2 or the fulminating or caseating type of shoulder tuberculosis associated with cold abscesses or sinus formation [4]. The atrophic type is further observed into 4 various types depending on the affections, i.e. Type I, the Caries sicca the atrophic form, Type II the Caries exudate with swelling and cold abscess formation and Type III the Caries mobile with good range of passive movements [3].
Case Report
A 55yrs old female patient who presented with a painful swelling with restriction of movements of the right shoulder since six months. Patient had taken various treatments without any relief; there was no history of trauma, weight loss, recent infection in the past or any history of tuberculosis in family or contact with tubercular patient. Right shoulder revealed restricted movements; no local rise in temperature, tenderness was present over anterior and posterior aspect of the right shoulder diffusely. External rotation and abduction movements were restricted while adduction and flexion were not restricted. Power of the muscles was unaffected with no neurological deficit. Antero-posterior and axial X-rays of the right shoulder showed no bony involvement however, ultrasonography showed lipoma. Serological investigations showed a markedly raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate (73mm of fall in 1 hr) and a positive C-reactive protein. After pre-anaesthetic evaluation the patient was posted for excision of the mass for which supine position was given with the bolster under the right shoulder [Fig.1], deltopectoral approach was taken[Fig. 2] and further dissected [Fig. 3]which revealed rice bodies[Fig. 4] typically seen in tuberculosis. The fluid released along with the rice bodies was also collected and were sent for histopathological examination which showed bursitis with loose boodies and DNA PCR (positive) testing respectively, following which the patient was given a shoulder immobilizer and was started empirically on anti-tubercular treatment( Category I) for six months.
Discussion
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is responsible for almost all the cases of osteo-articular tuberculosis in India. Atypical mycobacteria, other than M. tuberculosis fiumanis or bovis have also been reported in bony lesions. Certain precipating factors responsible for transmission of atypical mycobacteria are trauma, local steroidal injection, iatrogenic, diabetes mellitus, poor nutrition, poor hygienic conditions, use of immuno- suppressive drugs, acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome. The gold standards for the diagnosis of osseous tuberculosis are culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from bone tissue, positive Ziehl-Neelsen staining [5] and positive DNA PCR (as in this case). The patient responds well to anti-tuberculosis regimens. Treatment includes standard antituberculosis drugs for six months or category-I under Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme as per as World Health Organisation Guideline for management of tuberculosis [1].
Conclusion
Though swelling associated with restriction of range of movements and pain is a rare clinical presentation of form of tuberculosis of the shoulder but cannot be ruled out completely without proper further evaluation of the condition with the help of serological as well as radiological means available.
References
1. Tuli S. M. Tuberculosis of the skeletal system. 2nd ed. New Delhi, Jaypee Brothers Medical Publisher (P) Ltd. 1993.
2. Sankaran B.Tuberculosis Of Bones & Joints; Ind. J. Tub., 1993, 40,109.
3. Patel PR, Patel DA, Thakker T,Shah K, Shah VB. Tuberculosis of shoulder joint. Indian J Ortho 2003; 37:7.
4. S. Kant, S. Kumar, S.K. Verma, . Sanjay, V. Sharma: Dry Type Of Tuberculosis Of Humerus: A Case Report. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007 Volume 7 Number 2. DOI: 10.5580/4f3.
5. Rooney JJ Jr, Crocco JA, Kramer S, Lyons HA: Further observations on tuberculin reactions in active tuberculosis. Am J Med 1976; 60:517-522.
|
How to Cite This Article: Deshmukh A, Deo S, Salgia AK, Agarwal T. A Rare Unusual Case Presentation of the Tuberculosis of the Shoulder Joint. Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2013 Oct-Dec ;3(4): 23-25. Available from: https://www.jocr.co.in/wp/2013/04/13/2250-0685-098-fulltext/ |
(Figure 1) | (Figure 2) | (Figure 3) | (Figure 4)
[Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]
[rate_this_page]
Dear Reader, We are very excited about New Features in JOCR. Please do let us know what you think by Clicking on the Sliding “Feedback Form” button on the <<< left of the page or sending a mail to us at editor.jocr@gmail.com