[box type=”bio”] What to Learn from this Article?[/box]
Complications related to the modularity of total hip arthroplasty components.
Case Report | Volume 5 | Issue 1 | JOCR Jan-March 2015 | Page 8-10 | Parvej Ahmed, Dinesh Kumar. DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.243
Authors: Parvej Ahmed[1], Dinesh Kumar[2]
[1] Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, LLRM Medical College, Meerut, U.P. India.
[2] Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, UPRIMS&R, Saifai, Etawah, U.P. India.
Address of Correspondence:
Dr. Dinesh Kumar, U.P.R.I.M.S.& R. Saifai, Etawah, Uttar Pradesh 206130. India. Email: dr.dinesh@hotmail.com
Abstract
Introduction: Modular total hip arthroplasty system are now widely used, as these components increase the flexibility during primary and revision total hip arthoplasty. But this modularity itself associated with some risk of intraoperative and postoperative complications.
Case Report: We report a case of late disassembly of a primary total arthroplasty in a 42 years old patient five years after the replacement surgery where the femoral head remained in the acetabular socket.
Conclusion: Femoral head should be solidly impacted onto the stem and confirm that it has been assembled correctly before reduction.
Keywords: Total hip arthroplasty, Head neck disassembly, modular femoral components complications.
Introduction
Modular total hip arthroplasty system now widely employed, that offer the advantage of increase flexibility in components selection during the surgery, but it introduce the risk of intraoperative errors in matching and disassembly of the components postoperatively [1,2]. We report a unusually late separation of a modular femoral head from the neck of a primary total hip arthroplasry.
Case report
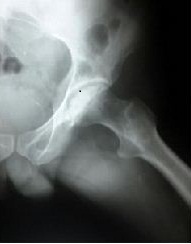
A 42 years old man, who had osteoarthritis of right hip (Fig 1), had an uncemented total hip replacement done through posterolateral approach.
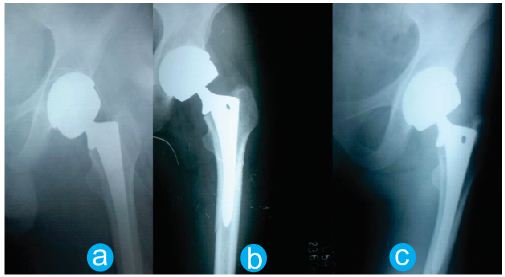
A porus coated, metal backed acetabular component with metal liner and a taper- locked modular femoral head with hydroxyapatite coated femoral stem were used. The femoral head was firmly impacted onto the neck . Stability was confirmed in both flexion and extension and the wound was closed. Initial results was excellent, the patient had no pain and could walk without supportive aids. The patient was regularly followed up to about five years and all the x-rays of those period were normal and had no abnormalities (Fig. 2,3).
- Figure 2: Showing radiographs at various Intervals. a-Immediate post-operative, b-One month post surgery and c-one year post surgery.
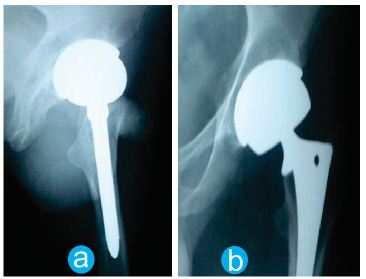
Five years after postoperatively, while the patient was rising from a chair, the patient experience a sudden click and followed by complete functional disability and impossibility to bear the weight. Standard radiograph showed disassembly of femoral neck and head while the head of prosthesis remained inside the acetabular socket. All the femoral and acetabular components visible in the x-ray are normal in appearance. There are no fracture lines in any components or complete fracture of any components or any other extra, abnormal sized or shaped metal piece visible in the x-ray (Fig. 4).
- Figure 4:
Anterio-posterior and Lateral radiograph of hip joints at five years after surgery. The modular femoral head disassembled from the stem and remained in the acetabular socket.
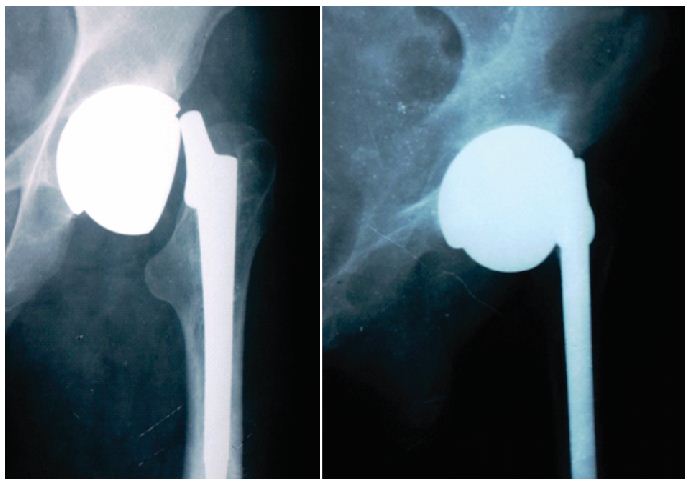
No subsidence could be observed. Open reduction was performed, same head was assembled onto the neck and the head was reduced into the acetabular socket. There was no evidence of visible corrosion of the interface between modular head and neck of femoral components. Intra-operative images are not available as that were not taken during the surgical procedure. Postoperative period was uneventful and a quick functional recovery was achived.
Discussion
Modularity in total hip arthroplasty has been benefit in term of allowing inventory reduction, while provide surgeon versatility intraoperatively and thus allowing optimal joint reconstruction [3], but it also introduce the risk of failure at the interfaces [1,2,3,4,5,6].
Modular femoral head may disassemble during close reduction of a dislocated prosthesis or during normal activity [1] such as in case report of current study.
We suspect that the mechanism of this disassembly of femoral head was the sealed air that pushes back the stem neck and unlocks the taper lock. It is also possible that the head was not impacted adequately onto the stem intraoperatively.
Conclusion
As a result of this experience, certain recommendation can be made to prevent this type of complication. The taper should be neatly clean and completely dry before the implantation of femoral head onto it. Blood, fluids or tissue fat layers should be completely removed from the taper. The femoral head should be solidly impacted with blow using a mallet. It is advised to use second blow as it may disengage the head if it was not placed centrically onto the taper, otherwise this second blow solidly lock the taper lock mechanism in a centrally placed head. Always confirm that, the head has been assembled correctly by applying manual distraction forces to femoral head.
Clinical Message
Disassembly of modular total hip arthroplasty system after surgery is rare, but it can occur in any case. Therefore, whenever using such type of arthroplasty system, all the precautionary measures should be taken during surgery which are necessary to prevent such type of complication..
References
1. Karaismailoglu TN, Tomak Y, Gulman B. Late detachment modular femoral component after primary total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2001;121:481-82.
2. Barrack RL, Burke DW, Cook SD, et al. Complications related to modularity of total hip components. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75:688-92.
3. Chmell MJ, Rispler D, Poss R. The impact of modularity in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 1995;319:70-84.
4. Woolson ST, Puttort GT. Disassembly of a modular femoral prosthesis after dislocation of the femoral component: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1990;72:624-25.
5. Star MJ, Colwell CW, Donaldson WF, et al. Dissociation of modular hip arthroplasty components after dislocation. Clin Orthop 1992;278:111-15.
6. Regis D, Modena M, Danesi G, et al. Head-neck disassembly of an uncemented revision stem treated by addition of a proximal spacer. Acta Orthop Belg 2003;69:463-66.
| How to Cite This Article: Ahmed P, Kumar D. Late Disassembly of Femoral Head and Neck of A Modular Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2015 Jan-March;5(1): 8-10. Available from: https://www.jocr.co.in/wp/2015/01/28/2250-0685-243-fulltext/ |
[Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF] [XML]
[rate_this_page]
Dear Reader, We are very excited about New Features in JOCR. Please do let us know what you think by Clicking on the Sliding “Feedback Form” button on the <<< left of the page or sending a mail to us at editor.jocr@gmail.com