Distal trimalleolar fracture of ankle fixed with Ilizarov and bone graft provides better stability than plating to prevent non-union, especially in elder patients as early as possible.
Dr. Mohamed Safiullah, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Balaji Medical College, Chennai - 600 044, Tamil Nadu, India. E-mail: dr.safiullahmbbsms@gmail.com
Introduction: Orthopedic surgeons have long acknowledged the difficulty of treating distal tibia and fibula fractures with lateral malleoli fractures in individuals with medical comorbidities due to a lack of inadequate blood supply. Aged Type 2 diabetic individuals, with distal tibia and fibula fracture with lateral malleoli fracture, are more prone to complications such as non-union, wound infection, and delayed bone healing. It is debatable whether surgical or non-invasive treatment is preferable for diabetic complex fractures.
Case Report: A 62-year-old male suffered a right distal tibia and fibula fracture with lateral malleoli fracture following an incidental fall followed by a hit over the iron rod. The patient was treated conservatively with POP for 6 weeks due to the patient’s refusal of surgical management. Radiography after 6 weeks revealed features of non-union.
Conclusion: The Ilizarov external fixation with bone graft was planned later to treat the non-union distal tibia and fibula fracture with lateral malleoli fracture. About 18 months after the Ilizarov fixation radiography reviewed the features of the union and clinically also patient improved.
Keywords: Ilizarov ring fixator, distal tibia and fibula fracture with lateral malleoli fracture, non-union, Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Complex fractures such as the distal tibia and fibula fractures with lateral malleoli fractures are more prone to non-union, especially in elderly patients with medical comorbidities due to inadequate blood supply [1-3]. Elder patients are more prone to post-operative complications such as surgical site wound infections, bed sores, pulmonary or fat embolism, and wound dehiscence, hence planning treatment for these patients is challenging. Ilizarov fixation reduces the complications which arise from both surgical and non-surgical treatment, especially in medically morbid patients, due to minimal soft-tissue handling and minimal blood loss [4-6]. Postoperatively, the radiological and clinical outcome is better with Ilizarov fixation.
A 62-year-old male sustained the incidental fall followed by a hit over the iron rod and was diagnosed with distal tibia and fibula fracture with lateral malleoli fracture. The patient was not willing to surgical fixation, and hence, the patient was treated conservatively with POP and the patient was asked for non-weight bearing. After 6 weeks of POP removal, radiographic features showed non-union of distal tibia and fibula with lateral malleoli. The patient was convinced then and planned for the Ilizarov fixation. 15 days after surgery, full weight-bearing walking was allowed. Serial X-rays were taken on follow-up, and radiography showed features of the union. After 18 months of the Ilizarov external fixator with bone graft, the patient improved clinically and radiologically. The patient was followed up for 2 years for assessment.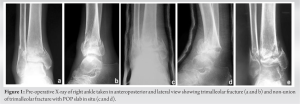
Elderly diabetic patients with bony fractures are more prone to complications such as non-union, infection, delayed bone healing, and bed sores, which threaten the patient’s life. Ilizarov fixator reduces the risk of complications due to minimal soft-tissue handling, minimal blood loss, and early mobilization [7-10]. Incidence of post-operative surgical site wound infection is less in external fixation as compared to open reduction with internal fixation, especially in elderly diabetic patients [10-12]. Thus early mobilization and reduced post-operative complications make the Ilizarov external fixator more feasible for the elderly diabetic patient, especially in distal tibia and fibula fractures which lack adequate blood supply.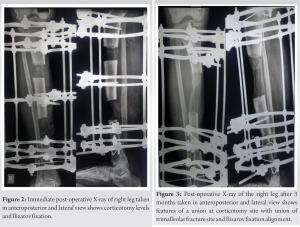
A complex distal tibia and fibula fracture with lateral malleoli fracture in aged diabetic patients are challenging for orthopedicians due to inadequate blood supply and medical comorbidities, which leads to various complications [13, 14]. Ilizarov fixation allows early mobilization, reduces the possible post-operative complications, and achieves the desired result of treatment.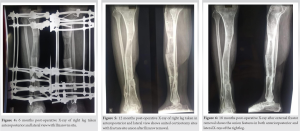
Ilizarov fixation with bone graft for trimalleolar fracture of the ankle in patients with medical comorbidities provides better stability and early mobilization with minimal complications than ORIF with plating or other modalities of treatment.
References
- 1.Chaudhary SB, Liporace FA, Gandhi A, Donley BG, Pinzur MS, Lin SS. Complications of ankle fracture in patients with diabetes. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2008;16:159-70. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wukich DK, Joseph A, Ryan M, Ramirez C, Irrgang JJ. Outcomes of ankle fractures in patients with uncomplicated versus complicated diabetes. Foot Ankle Int 2011;32:120-30. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Matsushita T, Watanabe Y. Chipping and lengthening technique for delayed unions and nonunions with shortening or bone loss. J Orthop Trauma 2007;21:404-6. [Google Scholar]
- 4.McCormack RG, Leith JM. Ankle fractures in diabetics: Complications of surgical management. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80:689-92. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Crist BD, Khazzam M, Murtha YM, Della Rocca GJ. Pilon fractures: Advances in surgical management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2011;19:612-22. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bacon S, Smith WR, Morgan SJ, Hasenboehler E, Philips G, Williams A, et al. A retrospective analysis of comminuted intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond: Open reduction and internal fixation versus external Ilizarov fixation. Injury 2011;39:196-202. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lovisetti G, Agus MA, Pace F, Capitani D, Sala F. Management of distal tibial intra-articular fractures with circular external fixation. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2009;4:1-6. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wyrsch B, McFerran MA, McAndrew M, Limbird TJ, Harper MC, Johnson KD, et al. Operative treatment of fractures of the tibial plafond. A randomized prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1996;78:1646-57. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tornetta P 3rd, Weinwer L, Bergman M, Watnik N, Steuer J, Kelley M, et al. Pilon fractures: Treatment with combined internal and external fixation. J Orthop Trauma 1993;7:489-96. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Górski R, Żarek S, Modzelewski P, Małdyk P, Wiśniewski R, Górski R. Open trimalleolar fractures treated with ilizarov external fixator. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 2015;17:381-91. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Borzunov DY, Kolchin SN, Malkova TA. Role of the Ilizarov non-free bone plasty in the management of long bone defects and nonunion: Problems solved and unsolved. World J Orthop 2020;11:304-18. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dendrinos GK, Kontos S, Lyritsis E. Use of the Ilizarov technique for treatment of non-union of the tibia associated with infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:835-46. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Szelerski Ł, Pajchert Kozłowska A, Żarek S, Górski R, Mochocki K, Dejnek M, et al. A new criterion for assessing Ilizarov treatment outcomes in nonunion of the tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2021;141:879-89. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chan MC, Khan SA. Ilizarov reconstruction of chronic bilateral calcaneovalgus deformities. Chin J Traumatol 2019;22:202-6. [Google Scholar]